Introduction to Yala National Park (yala safari)
Yala National Park, located in the southeastern region of Sri Lanka, is one of the most renowned wildlife sanctuaries in the country. Established in 1938, it spans over 979 square kilometers, making it the second largest national park in Sri Lanka. The park is bordered by the Indian Ocean to the south, providing unique coastal ecosystems that complement its diverse landscapes of jungles, wetlands, and scrublands. This variety of habitats is crucial in supporting an extensive range of flora and fauna, positioning Yala as a premier destination for wildlife tours Sri Lanka.
Yala is distinguished by its rich biodiversity and is home to an array of wildlife species that inhabit its distinct ecosystems. The park is particularly famous for its significant population of Sri Lankan leopards, offering visitors an exceptional opportunity to observe these elusive animals in their natural habitat. Besides leopards, visitors may also encounter a wide variety of other yala national park animals including elephants, sloth bears, and numerous bird species, adding to the allure of the yala wildlife safari.
Another notable aspect of Yala National Park is its conservation efforts aimed at protecting endangered species and their habitats. The park not only attracts tourists seeking adventure and wildlife sightings but also serves as a crucial area for research and conservation initiatives. The diverse environments within Yala foster unique ecosystems, providing important breeding grounds for various species. As a result, Yala National Park continues to play a vital role in Sri Lanka’s ecological balance and wildlife preservation.
The combination of exceptional biodiversity, coupled with the breathtaking landscapes of jungles and coastlines, ensures that Yala National Park remains a key destination for wildlife enthusiasts and nature lovers. With burgeoning interest in yala safari experiences, the park stands as a testament to the richness of Sri Lanka’s wildlife heritage.
The Majestic Sri Lankan Leopard
The Sri Lankan leopard (Panthera pardus kotiya) is a subspecies of leopard found exclusively in Sri Lanka, making it one of the most sought-after animals to observe during a Yala wildlife safari. Known for its stunning coat marked with black rosettes, this majestic feline has adapted remarkably to its surroundings, primarily inhabiting the dense forests and shrublands of Yala National Park. As the apex predator of the region, the Sri Lankan leopard plays a crucial role in maintaining the ecological balance.
Typically solitary in nature, these leopards exhibit nocturnal behaviors, primarily hunting at night. Their diet primarily consists of medium-sized mammals, including deer and wild boar, showcasing their impressive strength and hunting strategies. Utilizing stealth and camouflage, they stalk their prey with a calculated approach, demonstrating agility and prowess that are quite mesmerizing to witness during wildlife tours in Sri Lanka.
Finding a Sri Lankan leopard during a Yala safari can be a rewarding experience for nature enthusiasts. To increase chances of an encounter, it is advisable to visit during the early morning or late afternoon when these elusive cats tend to be more active. Additionally, keeping a keen eye on the trees and rocky outcrops can be beneficial, as leopards often rest in elevated areas, staying out of sight while they survey their surroundings.
Despite their impressive adaptations, Sri Lankan leopards do face threats primarily due to habitat loss and poaching. Conservation efforts are in place to protect this incredible species, making it imperative for safari-goers to engage responsibly with wildlife. By partaking in regulated safaris, individuals contribute to the preservation of these magnificent Yala National Park animals and their habitats, ensuring that future generations can admire their elusive beauty.
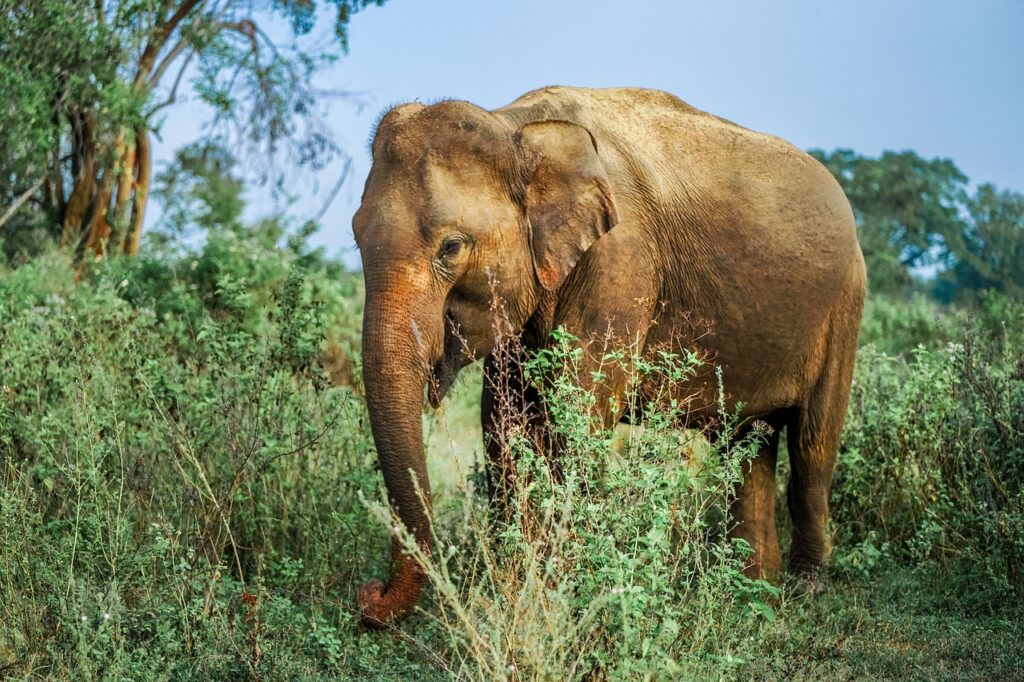
Introducing the Elephants of Yala
The Asian elephants that inhabit Yala National Park are among the most captivating wildlife species that visitors encounter during their Yala wildlife safari. These majestic creatures are known for their complex social structures, which typically revolve around matriarchal groups. A female elephant forms the core of a herd, leading and nurturing her young along with other females and their offspring. This social network can comprise of several generations, providing stability and learning opportunities for younger elephants as they navigate their surroundings.
Daily habits of the elephants in Yala are dictated largely by the availability of food and water. These giants primarily graze on grasses, leaves, and bark, spending a considerable portion of the day foraging. They can consume up to 300 pounds of vegetation daily, necessitating their nomadic lifestyle. Moreover, their movements are influenced by the seasonal changes in their habitat, often traveling long distances in search of more abundant resources during dry periods.
For those embarking on wildlife tours in Sri Lanka, the best times to observe these incredible animals are typically early in the morning and late in the afternoon. During these cooler parts of the day, elephants are more active, providing visitors an excellent opportunity to witness their behavior in the wild. Observing them drinking at watering holes or bathing in the mud can be an unforgettable highlight of the safari experience. Interestingly, elephants are known to interact with various other species in Yala, often playing a role in the ecosystem by helping to maintain habitats for other animals. This interspecies relationship enhances the biodiversity critical to Yala National Park, making it a vital area for wildlife conservation.
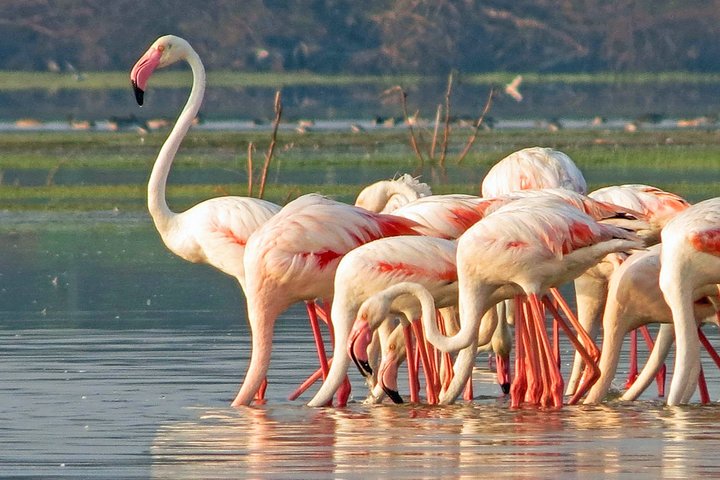
The Colorful Avifauna of Yala
Yala National Park, renowned for its diverse wildlife and stunning landscapes, is also celebrated for its impressive collection of avifauna. The park is home to a variety of both resident and migratory bird species, making it a paradise for birdwatchers and nature enthusiasts alike. Among the prominent species, the Sri Lankan Junglefowl stands out with its vibrant plumage, emblematic of the region’s beauty. This striking bird is a national symbol and is often spotted in the park’s dense shrublands, where it forages for food.
Another notable resident is the Crested Serpent Eagle, a formidable and majestic bird that can be seen gliding over the park’s grasslands and forests. Its distinctive call and soaring flight make it a favorite among birdwatchers. Visitors may also encounter the Chestnut-headed Bee-eater, known for its dazzling colors and aerial acrobatics as it feeds on bees and other insects. In addition to these fascinating residents, Yala serves as a critical stopover for many migratory species, with some traveling thousands of miles to breed and feed.
For those looking to enhance their birdwatching experience during a Yala wildlife safari, it is advisable to visit during the early morning or late afternoon when birds are most active. Silence and patience are essential, as they help in spotting elusive species. Bringing binoculars and a field guide can greatly enhance the enjoyment of exploring Yala’s avifauna. Additionally, many wildlife tours in Sri Lanka offer specialized birdwatching trips tailored to enthusiasts, ensuring a comprehensive experience of this rich biodiversity.
Spotting the Sloth Bear
Among the intriguing wildlife species that populate Yala National Park, the Sloth Bear stands out as a unique and captivating creature. Known for their shaggy fur and distinctive claws, these bears are primarily nocturnal, which means they are more active during the night and prefer to rest in dense forested areas during the day. A key aspect of Yala wildlife safari tours is the opportunity to observe these fascinating animals in their natural habitat.
The diet of the Sloth Bear mainly consists of insects, fruits, and honey, showcasing their role as essential contributors to the ecosystem. Their foraging behavior often involves tearing apart tree bark and digging in the ground to uncover ants and termites. This not only satisfies their dietary needs but also benefits the environment by aerating the soil and allowing for the growth of new plant life. If you are fortunate enough to spot a Sloth Bear during your visit to Yala, you may observe their characteristic movements and hear the soft sounds they make as they search for food.
Recognizing the tracks of a Sloth Bear can enhance the experience of wildlife tours in Sri Lanka. Their large paw prints, measuring up to 10 inches in length, coupled with claw marks, can often lead to a sighting. Look for overturned rocks or disturbed soil, as these signs often indicate a bear’s recent foraging activity. Despite their somewhat clumsy demeanor, Sloth Bears are agile climbers and can often be spotted in the trees seeking out honeycomb.
Protecting the vulnerable Sloth Bear and its habitat is crucial for maintaining the ecological balance within Yala National Park. Conservation efforts are vital to ensure that these unique animals can continue to thrive in their natural environment. Understanding their role not only emphasizes the importance of wildlife preservation but also enriches the experience for visitors engaging in the Yala safari adventures.
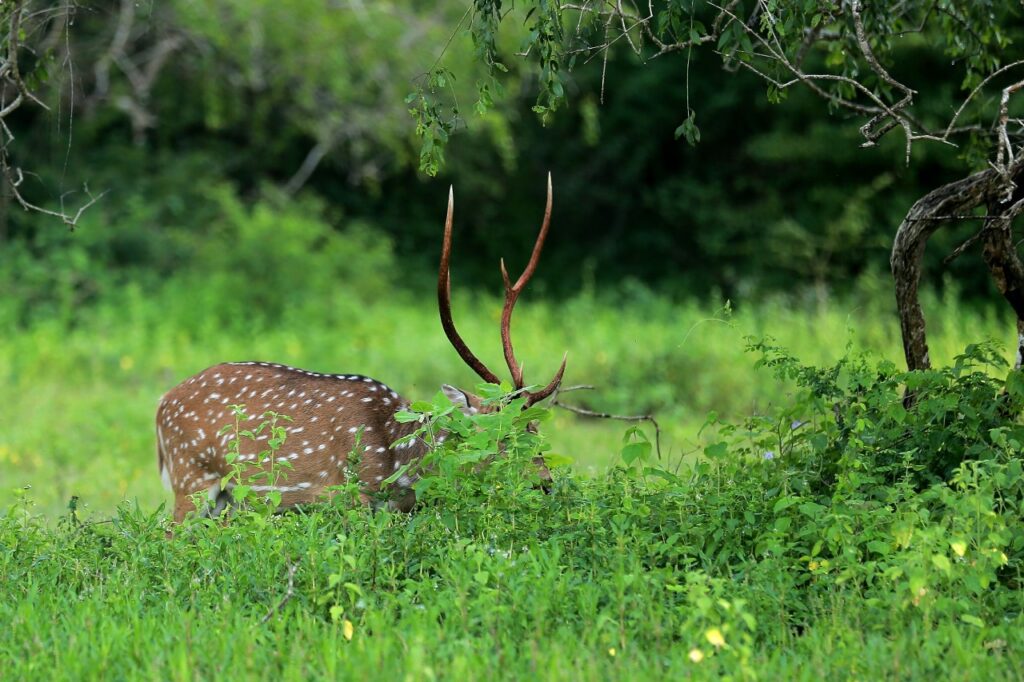
The Graceful Sambar Deer
The Sambar Deer (Cervus unicolor) is a prominent, graceful herbivore frequently spotted in Yala National Park, contributing significantly to the park’s vibrant ecosystem. With their long legs and large bodies, these deer are well-adapted to their surroundings, primarily inhabiting grasslands and the edges of dense forests. Their presence in the park not only highlights the diverse wildlife but also plays a crucial role in the ecological balance. As grazers, Sambar Deer feed on a variety of vegetation, including grasses, fruits, and leaves, impacting the growth of plant communities in Yala.
Sambar Deer are an essential prey species in the food chain, creating a vital link between herbivores and predators. Predators such as leopards, which are also commonly found in Yala, depend on Sambar Deer for sustenance. The interaction between these species showcases nature’s complex relationships and underscores the necessity of wildlife conservation. While Sambar Deer are known for their large size and impressive antlers—particularly in males—these attributes can also serve as a defense mechanism against potential threats in the wild.
To enhance your experience while on a Yala wildlife safari, it is beneficial to familiarize yourself with the optimal locations for spotting these majestic creatures. Sambar Deer are often seen near water bodies, especially during early mornings and late afternoons when they come to drink. The park’s diverse habitats provide many vantage points, making it easier for wildlife enthusiasts and photographers to immerse themselves in the natural beauty of Yala. Participating in wildlife tours in Sri Lanka offers further opportunities to witness these incredible animals in their natural habitat, ensuring an unforgettable adventure in the heart of Yala National Park.
The Striking Saltwater Crocodile
The saltwater crocodile (Crocodylus porosus) is one of the most captivating and formidable inhabitants of Yala National Park, known for being the largest living reptile species in the world. Found predominantly in coastal regions, saltwater crocodiles thrive in the brackish waters that are characteristic of the park’s lagoons and river mouths. Their impressive size and unique adaptations make them a key species in the park’s biodiversity, providing a critical insight into the ecosystem.
These reptiles are ambush predators, exhibiting remarkable patience and stealth when hunting. Their primary diet consists of fish, birds, and small mammals, but larger specimens are known to take down more substantial prey, including deer and even wild boar. This predatory behavior plays a vital role in maintaining the ecological balance within Yala, as they help regulate the population of various species. Observing these magnificent creatures in their natural habitat during a Yala wildlife safari can be an exhilarating experience, though it requires an understanding of their behavior and habitat.
Unfortunately, conservation challenges persist for saltwater crocodiles, primarily due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict. As a result, their populations face significant threats, underscoring the importance of protective measures within Yala National Park. Tourists engaging in wildlife tours in Sri Lanka are urged to follow safety precautions while observing these reptiles. Maintaining a safe distance and respecting their space is crucial, as saltwater crocodiles can be unpredictable and potentially aggressive if they feel threatened.
Through continued conservation efforts and responsible tourism practices, the coexistence of humans and these striking reptiles can be safeguarded, enriching both wildlife enthusiasts’ experiences and the protection of Yala’s delicate ecosystems.
Reptiles and Amphibians of Yala
The Yala National Park is not only renowned for its large mammals and avian diversity but also boasts a variety of reptiles and amphibians that contribute significantly to the park’s ecological balance. Among these species, the elusive chameleon often captures the attention of visitors. Known for their color-changing abilities, chameleons can blend seamlessly into their surroundings, making them challenging to spot. The best time for observing these fascinating creatures is during the early morning or late afternoon when they are most active.
Another notable reptile found in Yala is the Indian Python, which can grow to impressive lengths. This non-venomous constrictor plays a crucial role in controlling the population of small mammals and birds within the ecosystem. While on a Yala wildlife safari, keep an eye out for their unique patterns and large silhouettes basking in the sun. Additionally, the park is home to the Mugger Crocodile, often found lurking near water bodies, making it an essential species for studying both aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems.
Amphibians, such as the Sri Lankan Bull Frog and various species of tree frogs, also thrive within Yala’s diverse habitats. These amphibians are not only vital for pest control but are also indicators of environmental health. They exhibit unique adaptations that allow them to thrive in varying microhabitats within the park. To spot these creatures during wildlife tours in Sri Lanka, look for their distinctive calls during the wet season and along the edges of ponds and wetlands.
In conclusion, the reptiles and amphibians of Yala National Park offer an intriguing glimpse into the park’s biodiversity. Observing these remarkable species adds to the enriching experience of a Yala safari, showcasing the importance of conserving these habitats and their inhabitants.
Importance of Conservation Efforts in Yala
The ongoing conservation efforts in Yala National Park play a crucial role in safeguarding its unique ecosystems and diverse wildlife species. Yala is renowned for its rich biodiversity, which includes a variety of endemic and endangered animals. To maintain the delicate balance of this environment, dedicated management and protective strategies have been implemented. These initiatives focus on habitat preservation, anti-poaching measures, and community involvement to foster sustainable interactions between local populations and their natural surroundings.
One of the primary conservation programs in Yala involves regular monitoring of wildlife populations, specifically the iconic Yala National Park animals, including the elusive leopard and various species of birds. Such monitoring allows researchers to gather data on animal behavior, migration patterns, and overall health, leading to informed decisions regarding conservation practices. Wildlife tours in Sri Lanka, particularly those in Yala, emphasize the importance of education, raising awareness among visitors about the ecological significance of the park and promoting responsible wildlife viewing practices.
The role of local communities is integral to these conservation efforts, as they are the guardians of the park’s natural resources. Engaging locals in conservation initiatives minimizes human-wildlife conflict and ensures that the benefits of wildlife tourism are shared. For instance, community-led projects may include sustainable agriculture and eco-friendly business practices that support conservation while enhancing the livelihoods of residents. Visitors to Yala Safari can also contribute to wildlife protection by participating in these eco-conscious initiatives or supporting local conservation organizations financially. In doing so, they help to secure the future of this remarkable park and its inhabitants.
In conclusion, the conservation efforts at Yala National Park are essential for preserving its ecosystems and the diverse wildlife it houses. By working together, local communities, conservation organizations, and visitors can ensure that future generations will have the privilege of experiencing the wonders of Yala’s wildlife.